#
Administration
There are several components in the Web UI which allow maintenance of BDeploy. These are not to be used during normal operation by users. They are required during setup and to maintain current software versions of BDeploy itself if not done using the bdeploy remote-master CLI.
The administration dialogs are grouped into a Configuration, a Housekeeping and a Maintenance section.
#
Settings
In the Settings area some global settings can be configured.
#
General
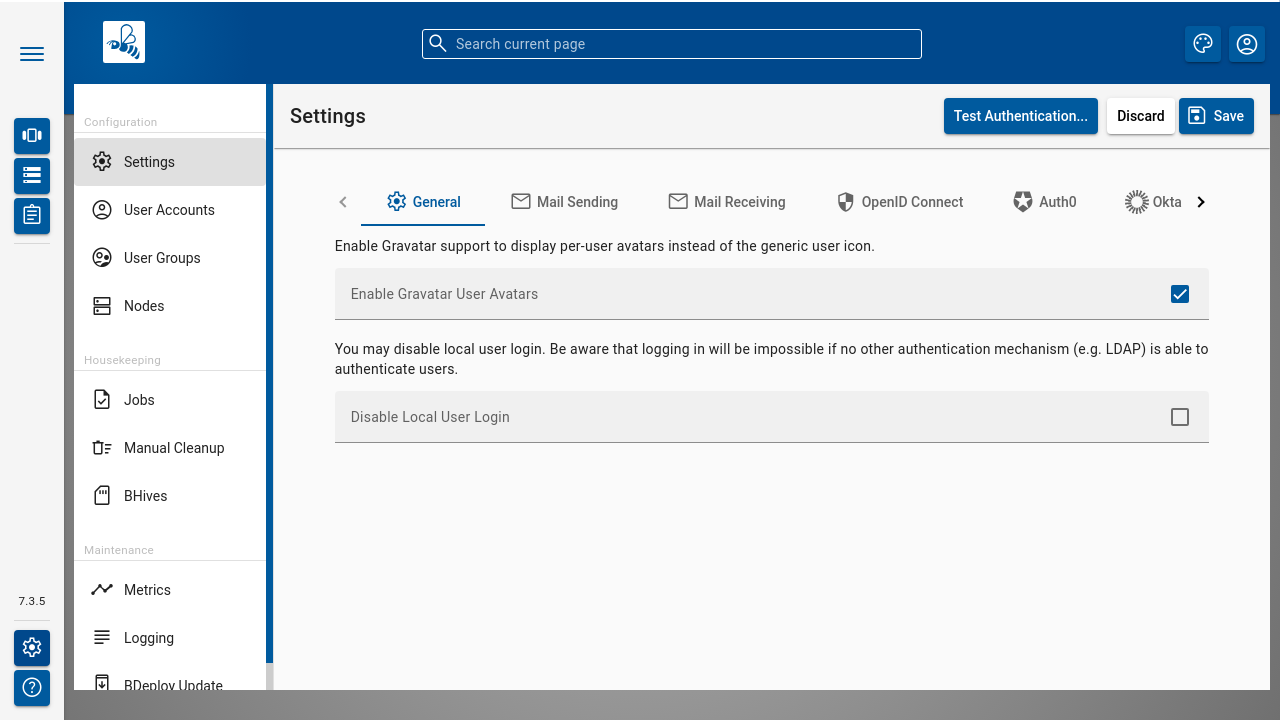
Gravatar support can be enabled here. If disabled, a generic icon is used for all users. Otherwise, BDeploy shows the Globally Recognized Avatar (or a substitute image) wherever a user icon is displayed in a dialog. Visit gravatar.com for more information.
BDeploy supports both built-in and external authentication mechanims. The built-in user authentication can be disabled completely in the settings.
Note
At least one login method must be configured. Disable local accounts only if it is ensured that at least one administrator account exists via external authentication!
#
OpenID Connect
OAuth2 with OpenID Connect support is available if enabled and configured. The URL must be the token endpoint of the OpenID Connect provider. For example, the URL may look something like this on Keycloak, depending on configuration:
https://auth.example.com/auth/realms/realmName/protocol/openid-connect/tokenThe Client ID and Client Secret are used to authenticate with the OpenID Connect provider, and need to be obtained from the OpenID Connect provider.
#
Auth0
Auth0 is an OpenID Connect compliant authentication provider. BDeploy can be configured to use it through the Authorization Code Flow. Configure an application as "Single Page Application" in the auth0 tenant, and provide the required information in the configuration page.
#
Okta
Okta is an OpenID Connect compliant authentication provider. BDeploy can be configured to authenticate users against Okta using its own proprietary authentication flow in a popup. Same as auth0, Okta requires a configured tenant which has application type "Single Page Application" set.
#
LDAP Auth.
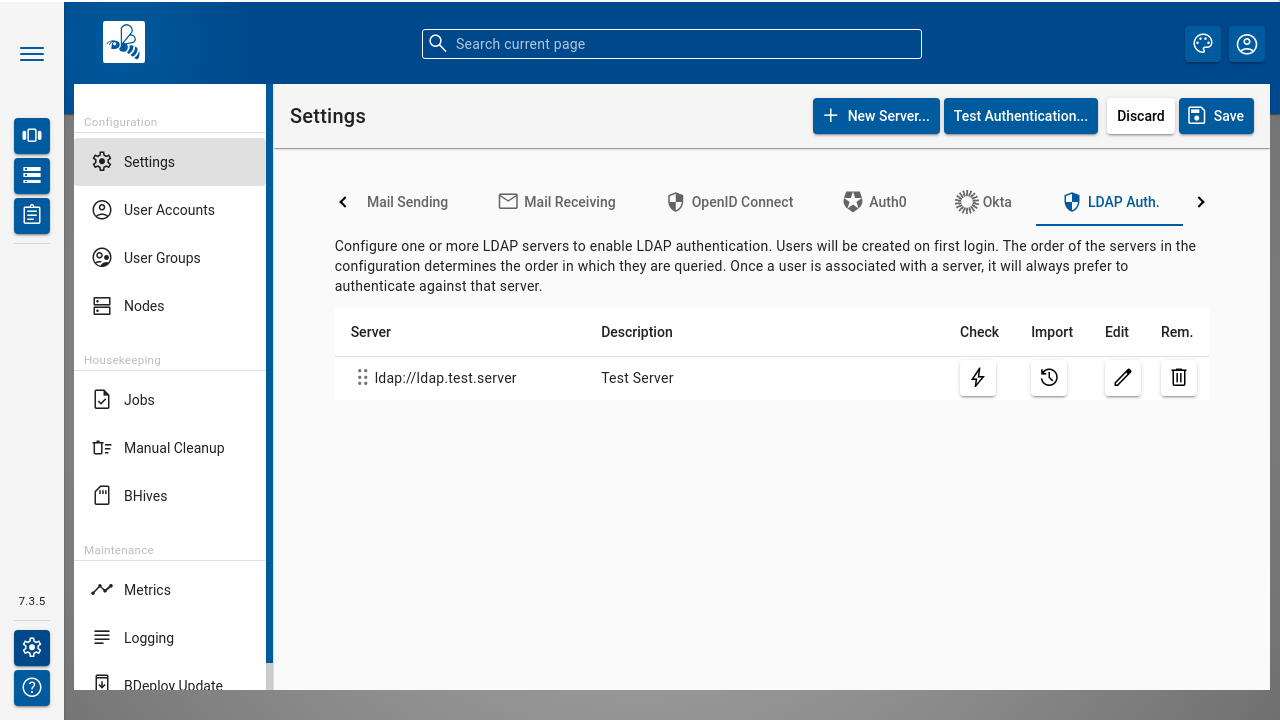
On the LDAP Auth tab, you can configure a list of LDAP servers which are queried when authenticating a user. Use drag and drop to specify the sort order in which the LDAP servers are queried for users that log on.
Tip
Technical experts can use the Check action to test a single LDAP server entry: BDeploy tries to establish a connection to the configured server. Some logging information, especially Java Exceptions, are shown in a popup window. Similarly, the Test Auth. action can be used to trace the entire authentication of a user.
BDeploy uses simple bind to authenticate users. First, a simple bind is made with the configured User. This user must have permissions to list other users that should be able to log into BDeploy. This bind is used to query for a user where the Account User Field matches the user name to be authenticated. This can be any field like user, sAMAccountName, or even mail if you want users to log on using their e-mail address. Once the user to log on is found, its distinguished name is used to perform another simple bind using the provided password. Once this succeeds the user is authenticated and an according record is created in BDeploy. From that point on, permissions can be granted to the user.
#
LDAP Server Properties
The following properties can be configured for each LDAP Server:
#
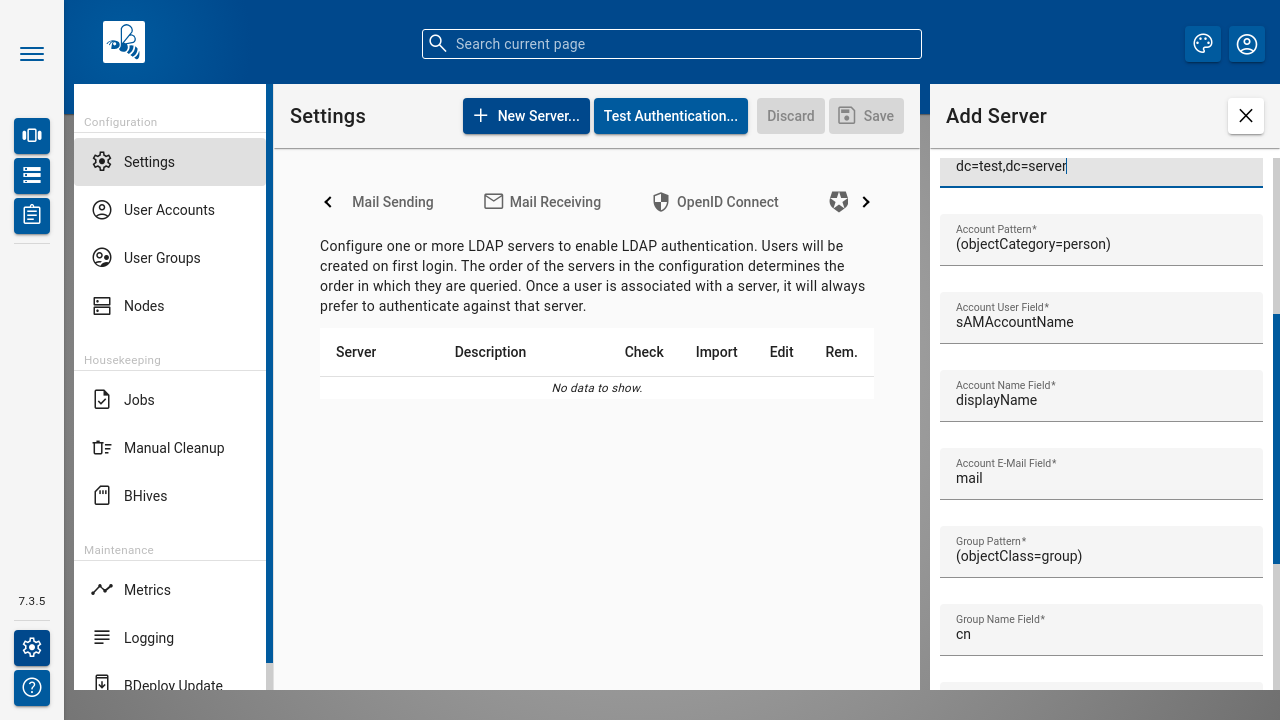
LDAP Import Users and Groups
To ensure a successful operation of the Import feature, it is essential to accurately configure the following fields: Account and Group Base, Account Pattern, Account User Field, Account Name Field, Account E-Mail Field, Group Pattern, Group Name Field, and Group Description.
Once these configurations are set up correctly, the import process becomes a straightforward task. Simply click on the Import action button, and BDeploy will seamlessly handle the rest. Should any errors occur during the import attempt, the system will promptly notify you of the encountered issues.
For added confidence, consider utilizing the Check action before initiating the Import process. This will help ensure a smooth connection to the LDAP Server and preemptively address any potential issues.
Tip
Using the Check action prior to Import can help verify the connectivity to the LDAP Server and preemptively identify any issues that might affect the import process.
#
LDAP Synchronization Job
The LDAP Synchronization Job periodically imports users and groups for LDAP connections with selected Periodically sync users and groups flag.
The job is identical to the Import action.
By default, job starts every midnight, but its schedule can be reconfigured via the CLI.
To reschedule a job use ldap --root=... "--setSyncSchedule=..." where setSyncSchedule is in cron format (e.g. 0 0 0 \* \* ? for midnight).
To check current schedule and last run timestamp use ldap --root=... --showSyncInfo.
#
LDAP Certificate Trust
Note
This section currently only applies to Linux installations.
If the configured LDAP server uses official certificates which are not trusted by the current JVM's default trust store, you can alternatively configure the BDeploy service to use the system cacert trust stores, which are typically available at a location like /etc/pki/ca-trust/extracted/java/cacerts. This path may be different on individual Linux distributions.
To use this trust store, you need to add these parameters to the command line of BDeploy:
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/etc/pki/ca-trust/extracted/java/cacerts -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeitYou can do so by means provided by the Linux distribution, e.g. directly editing the bdeploy.service systemd service file or setting BDEPLOY_OPTS environment variable to that value either globally or in a service environment file.
#
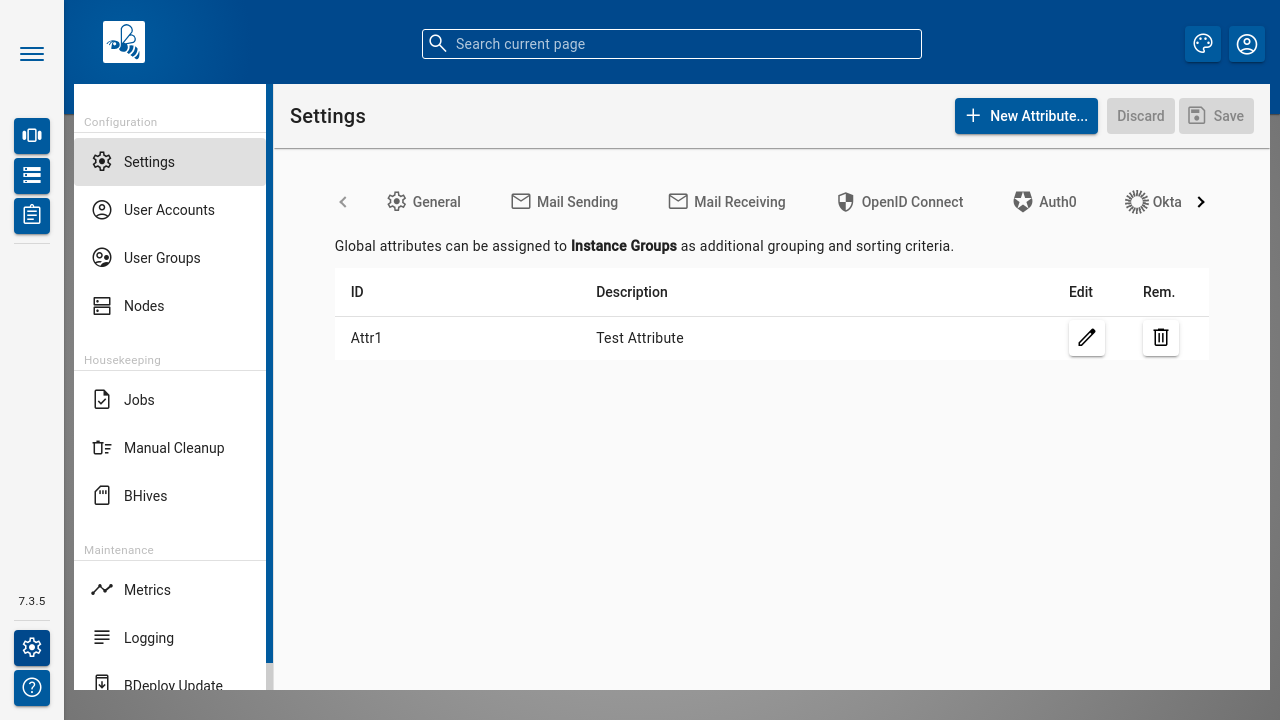
Global Attributes
In the Global Attributes tab, globally available attributes for Instance Groups can be maintained. Global attributes can be used to configure additional information for Instance Groups, which is then used as an additional grouping or sorting criteria.
#
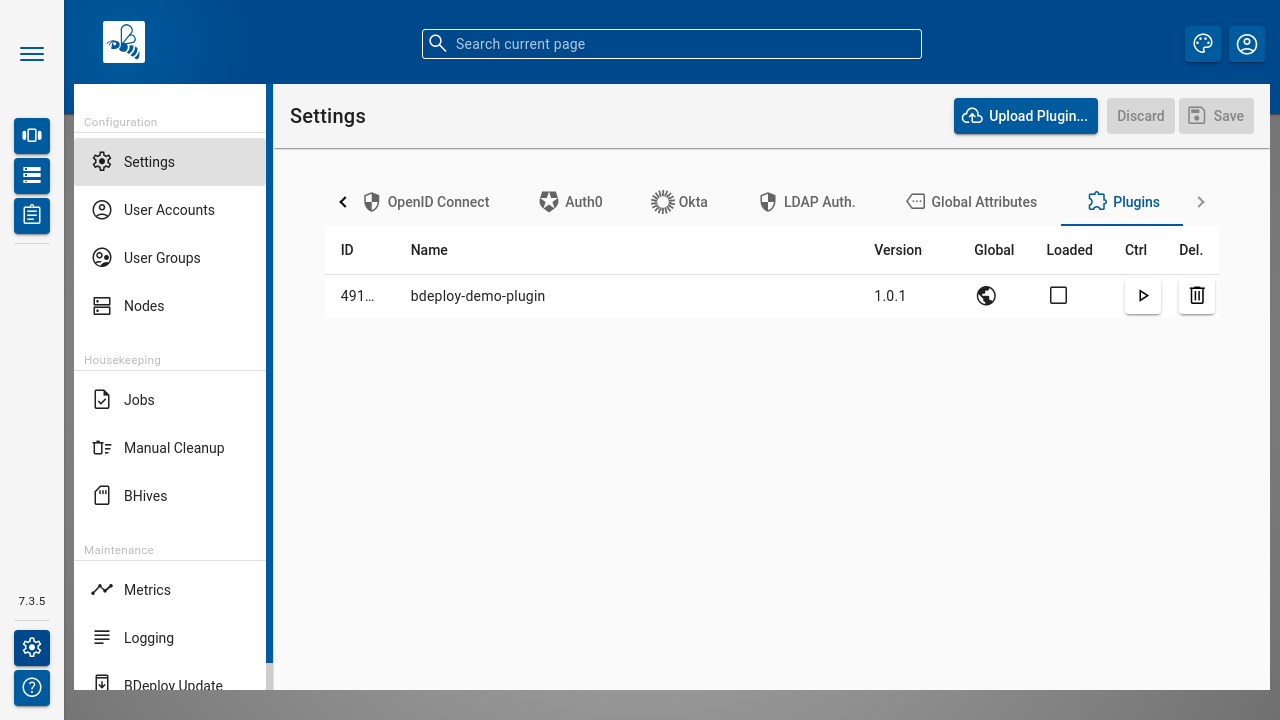
Plugins
The Plugins tab can be used to manage the plugins known by BDeploy. Plugins that are currently loaded can be stopped here. Via the Upload Plugin action global plugins can be uploaded. Global plugins can also be deleted from the system here.
#
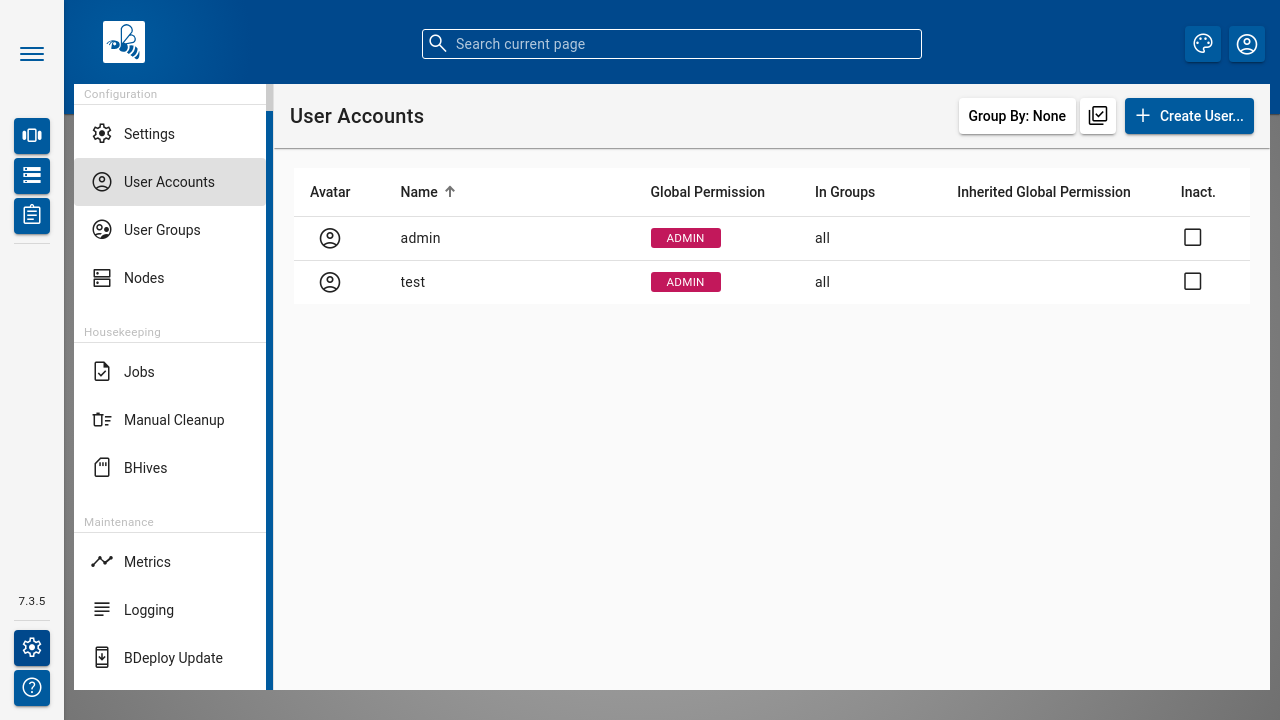
User Accounts
The User Accounts dialog lists all users known to the system, regardless of whether they are local users or LDAP users.
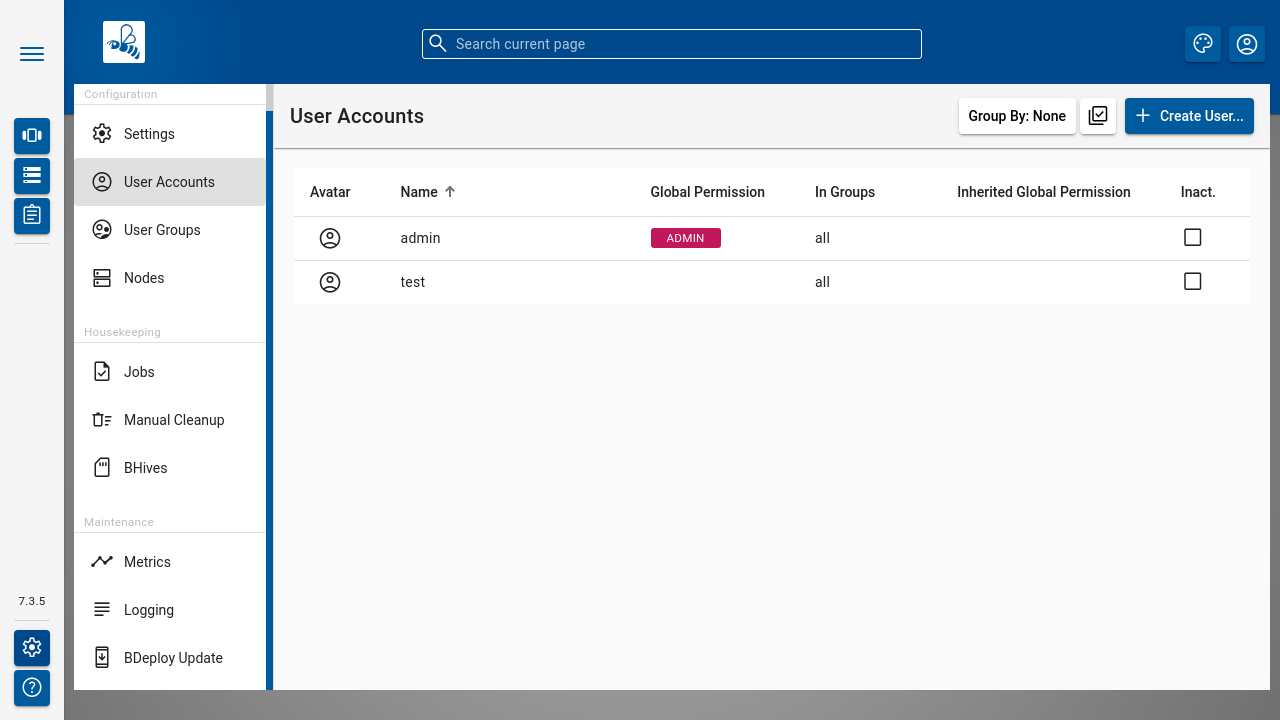
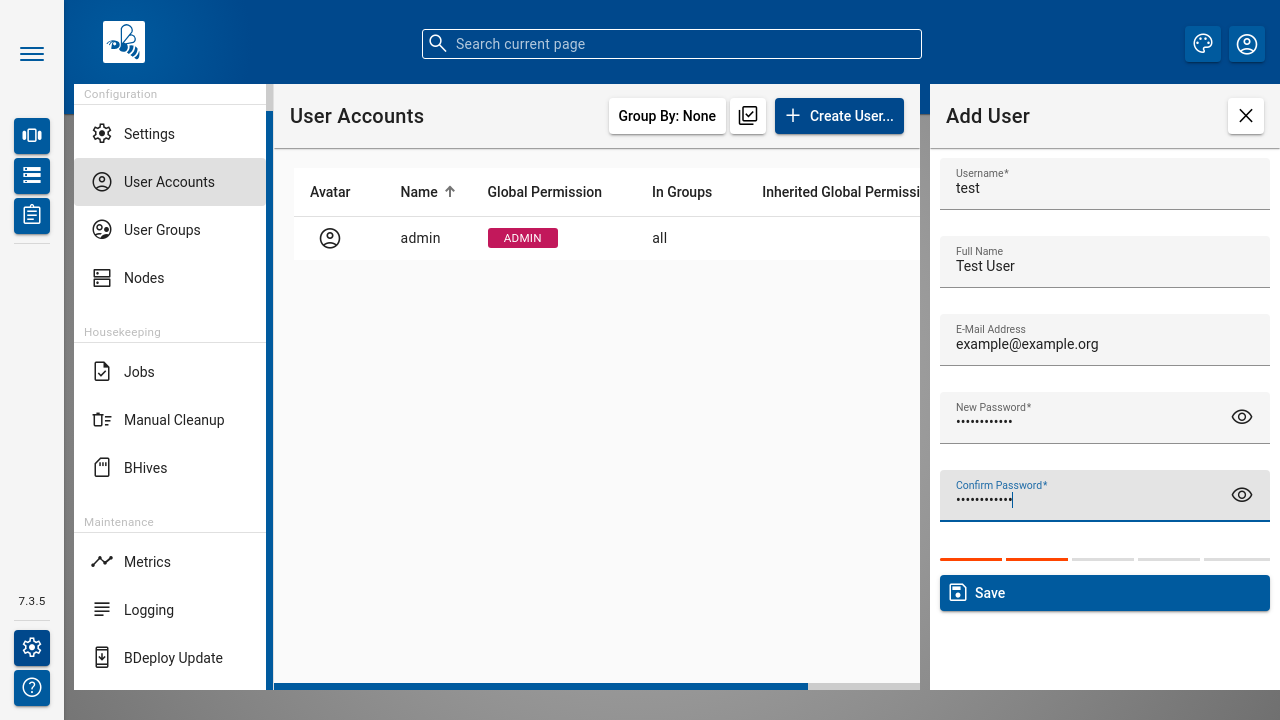
Use the [ Create User ] button to create a local user.
Once a User is available, you can click it to open the User Details panel where detailed information about the user, including a list of their permissions, is displayed.
Note
To protect against accidental lockout from the system, the currently logged in user cannot be changed, disabled or deleted.
The [ Deactivate Account ] and [ Activate Account ] buttons allow to deactivate/activate the selected user.
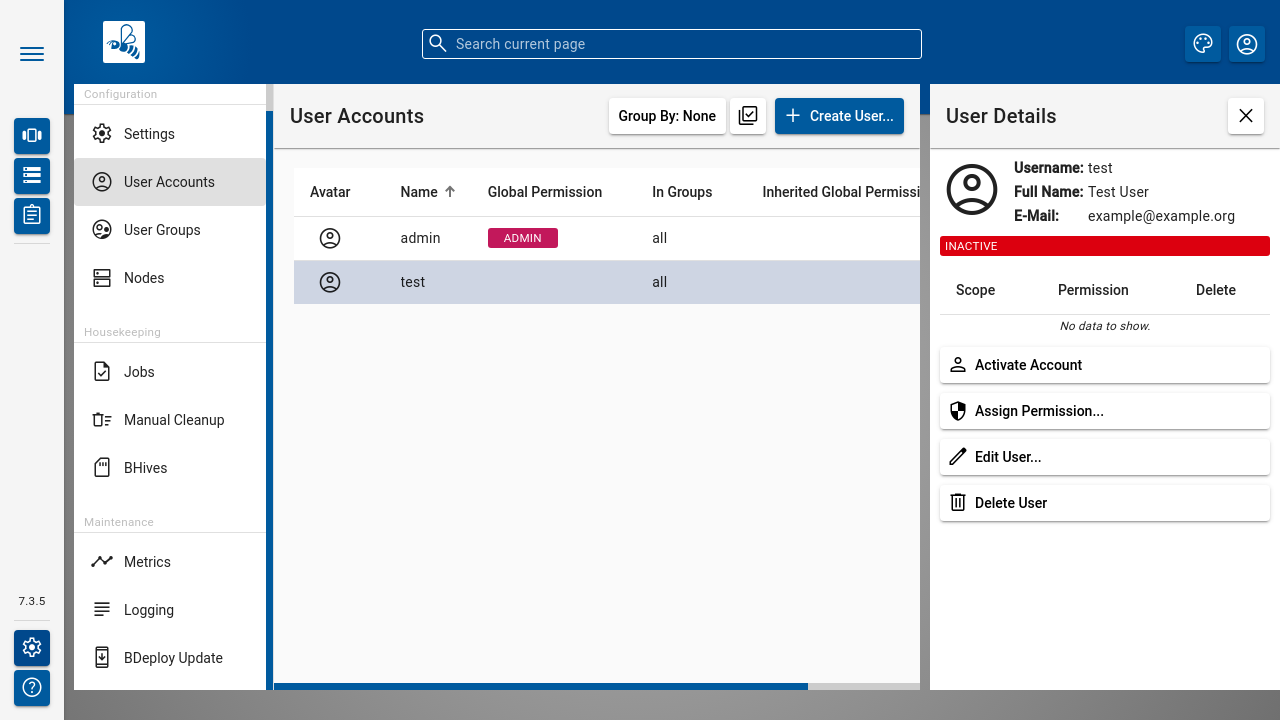
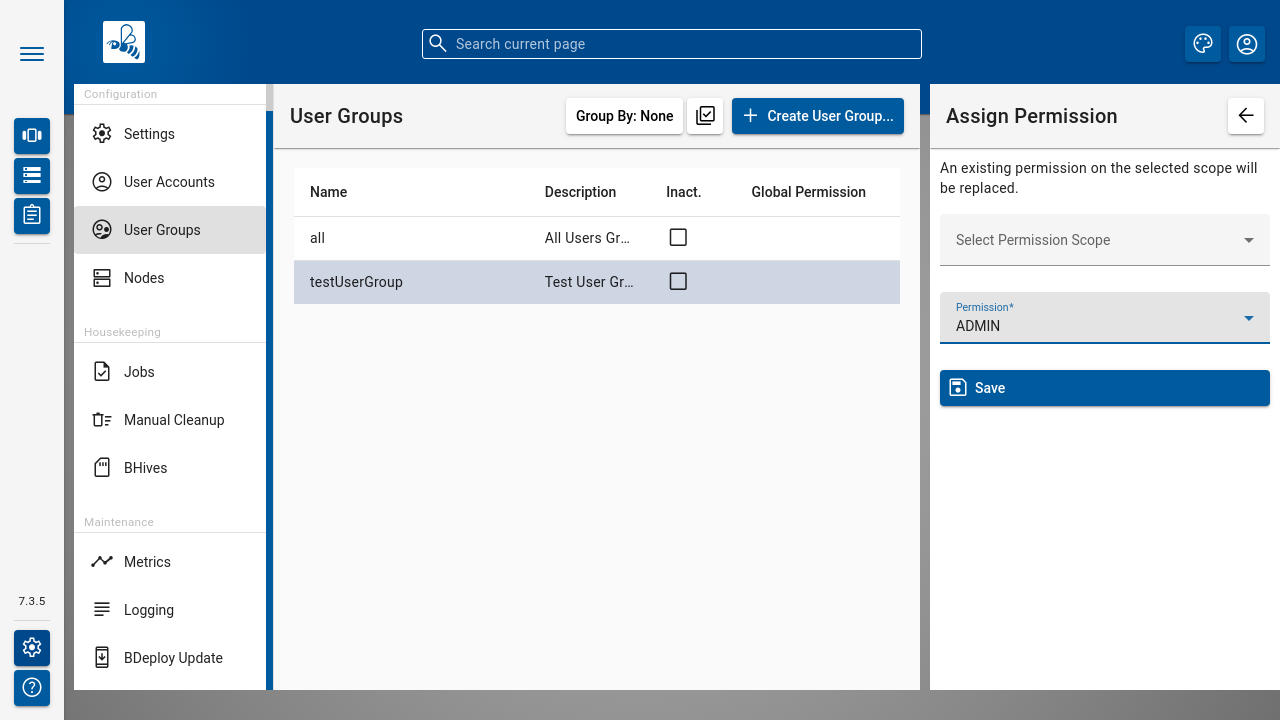
The [ Assign Permission ] opens a popup for adding a permission entry. Global permissions as well as scoped permissions on Instance Groups and Software Repositories can be maintained here.
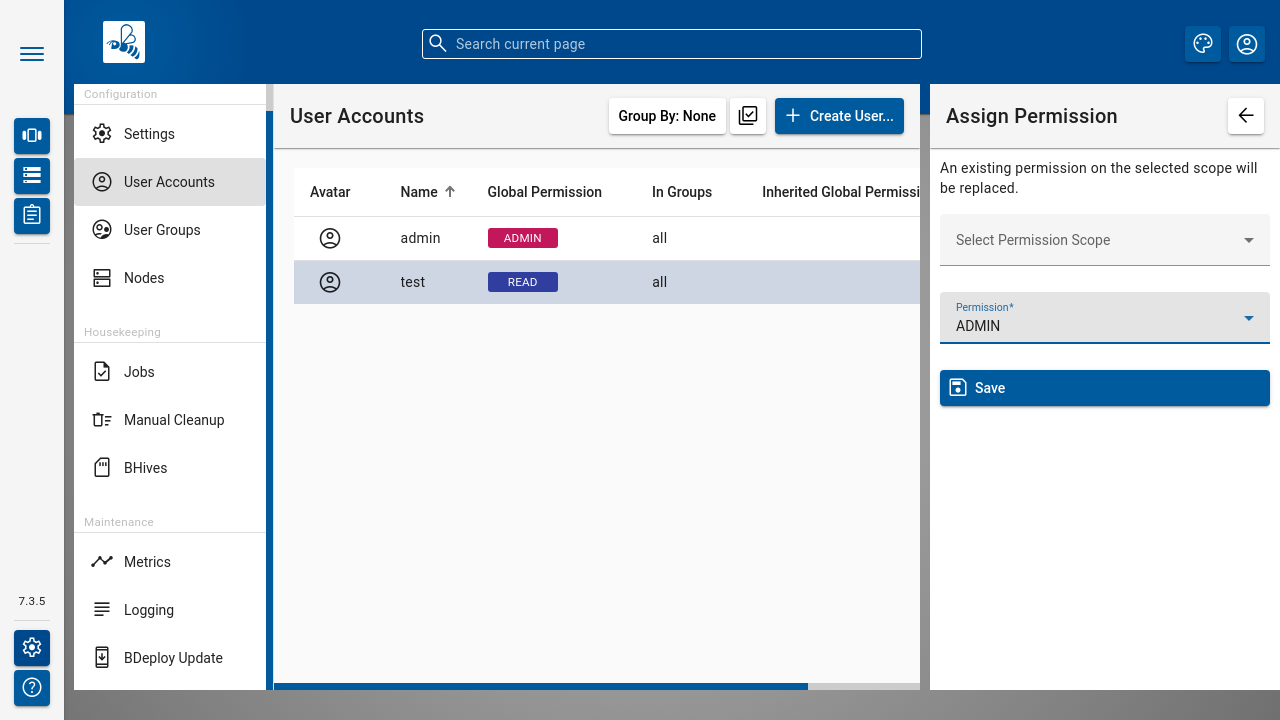
The [ Edit User ] opens a popup for editing the main user properties, as well as changing the password.
#
User Groups
BDeploy supports user groups. Their purpose is to simplify security management. By adding users to groups, administrators can efficiently manage access levels for multiple users in one place. All the permissions of an active user group will propagate to its users.
User Groups are managed the same way as User Accounts
The User Groups dialog lists all groups known in the system, regardless of whether they are local or LDAP groups.
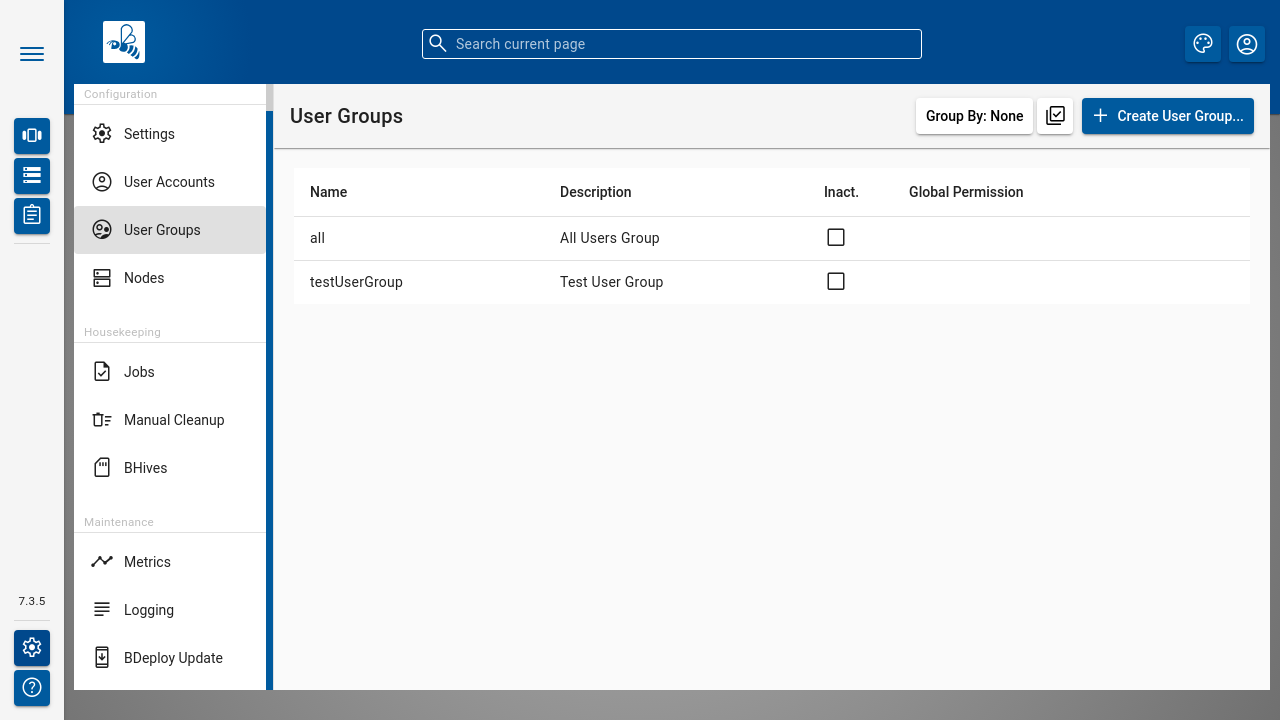
Use the [ Create User Group ] button to create a local user group.
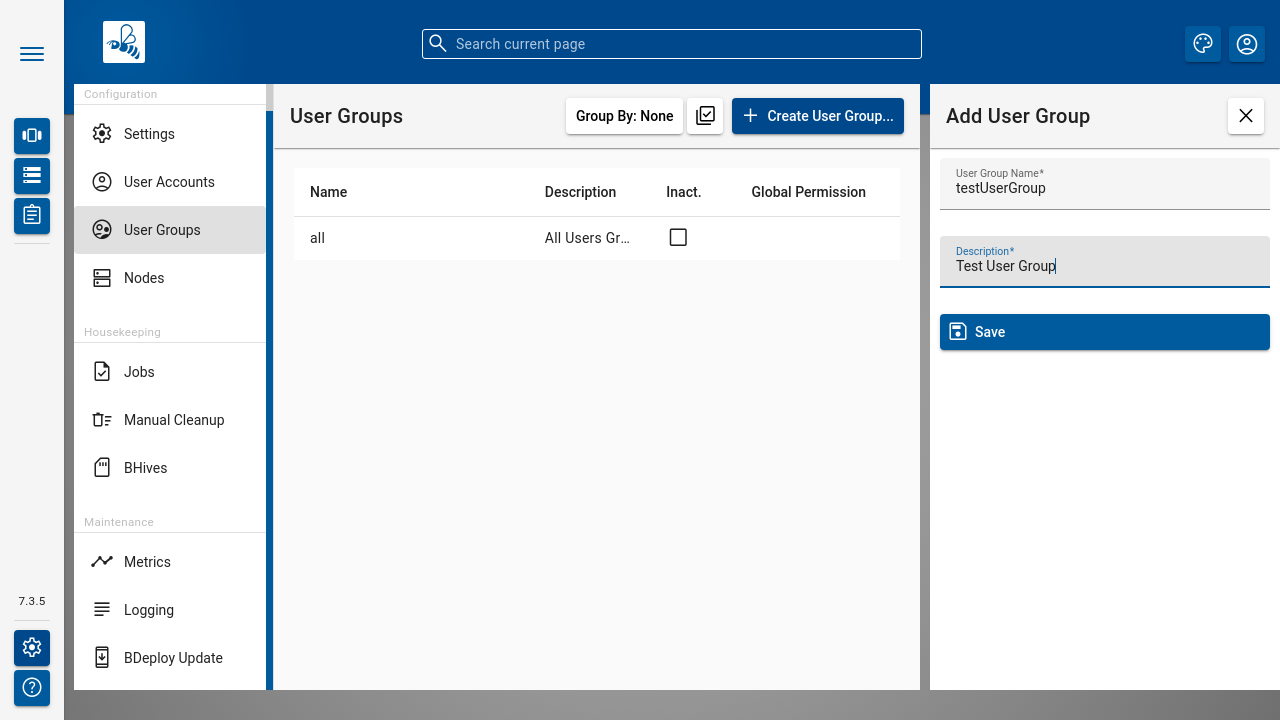
Once a User Group is available, you can click it to open User Group Details panel where detail information is shown on top along with users that belong to the group as well as the list of permissions.
The [ Deactivate Group ] and [ Activate Group ] buttons allow to deactivate/activate the selected group.
Use [ Add user to the group ] input to add user to the group. Enter user's login name and press [ + ] icon.
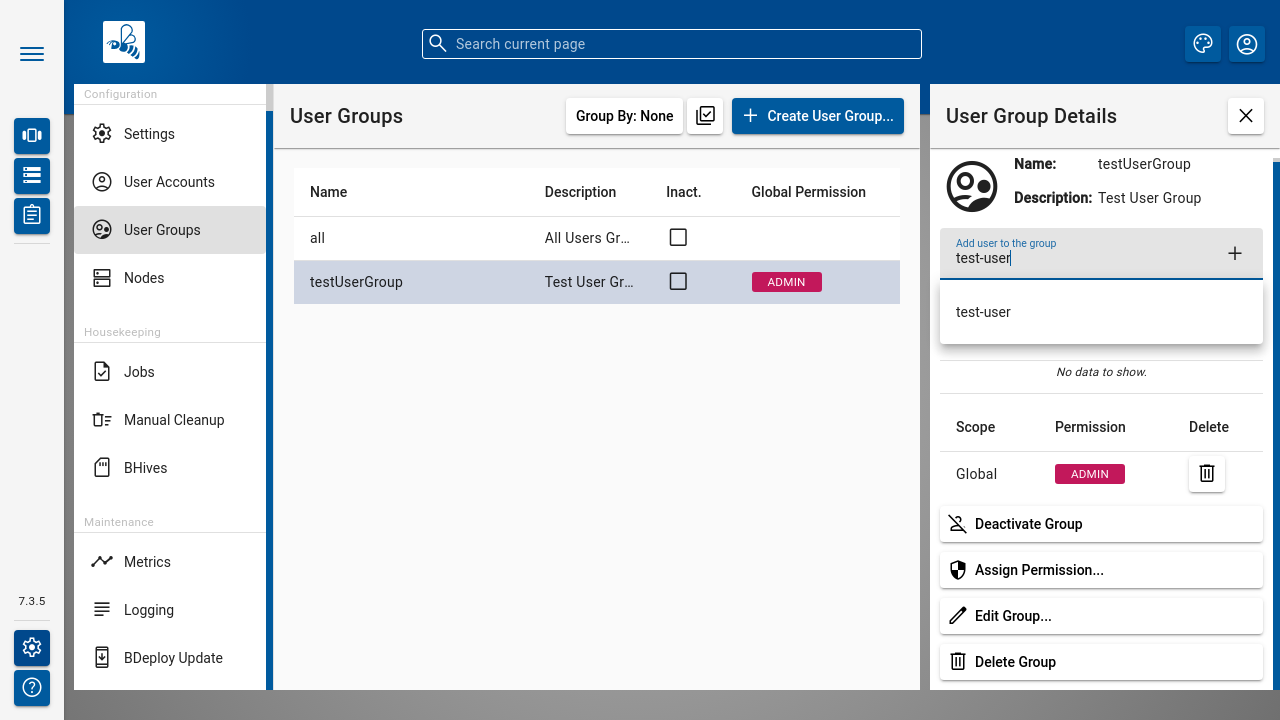
The [ Assign Permission ] opens a popup for adding a permission entry. Global permissions as well as scoped permissions on Instance Groups and Software Repositories can be maintained here.
#
All Users Group
There is a special All Users Group that cannot be deleted or deactivated, but its permissions can be edited. Every user, both present and future, is automatically enlisted in this group. You can make any Instance Group/Software Repository effectively public by assigning READ permission to All Users Group for Instance Group/Software Repository of your choice.
#
Manual Cleanup
You can use the Manual Cleanup page from the Administration menu to trigger a manual cleanup of stuff that is not needed any more. There is no need to trigger this manually as a job is scheduled that performs the exact same operation every night:
The dialog can be used to immediately trigger a cleanup and to reviewing of the actions performed before doing so.
Press the [ Calculate ] button to perform cleanup calculation. The result will be actions to be performed on Instance Groups or Nodes (including the Master). If no action is calculated at all, a corresponding message is displayed.
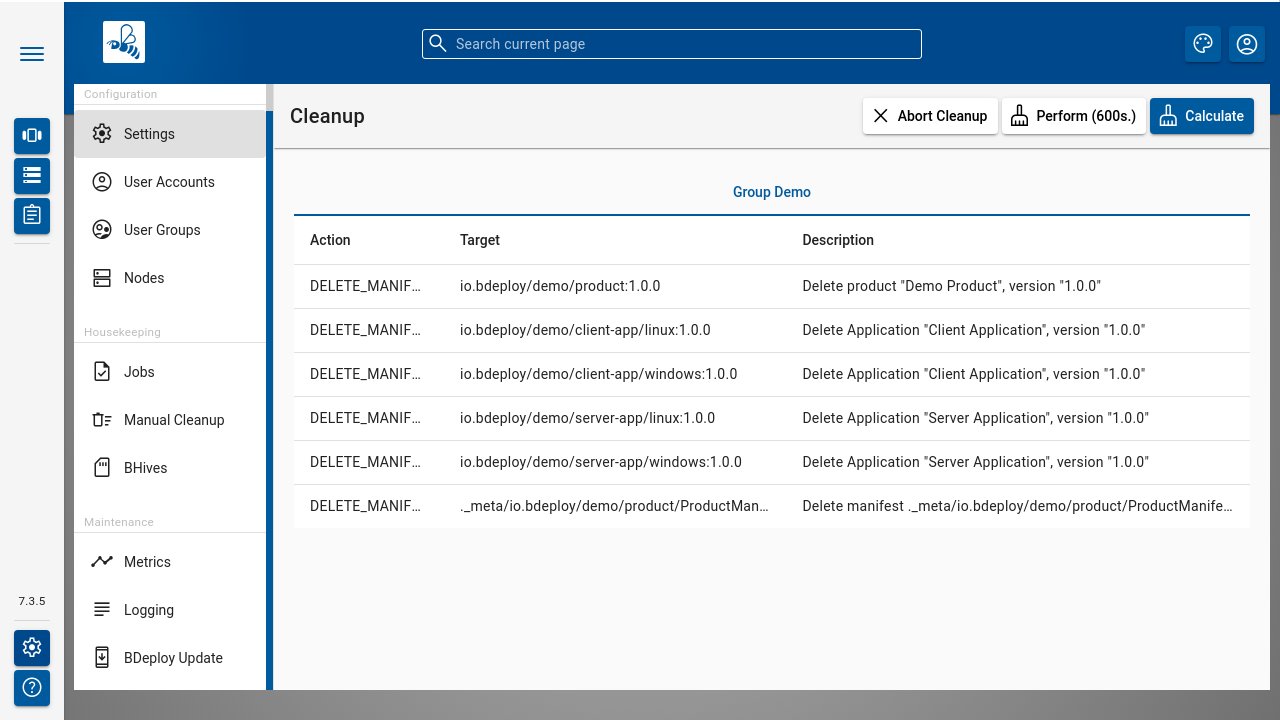
Press the [ Perform ] button to actually perform the calculated actions. The button [ Abort Cleanup ] resets the dialog without further actions.
Note
The dialog automatically resets itself after a certain timeout. This is to prevent execution of too old actions which might no longer be valid.
#
Hive Browser
The BHive page from the Administration menu is an internal tool for administrative purposes. It allows access to the internals of the BDeploy storage.
The table shows all available hives. The default hive is the internal storage where metadata about users and outer hives are stored. The actual data is stored in the individual hives itself.
Caution
It has the power to destroy everything - use with extreme caution.
Clicking a BHive opens the panel with maintenance actions
The details tab allows access to the Audit Logs and the content that is stored in a BHive. It also gives access to the repair and prune operations (see CLI) from the web interface.
#
Metrics
This dialog provides a quick way to investigate potential performance issues in the server itself by providing access to the in-memory metrics kept by the server for all actions.
The SERVER metrics will show various system information about the Java Virtual Machine of the master hosting the Web UI.
#
Logging
The logging page allows to view and download the master servers main audit log, which includes information about tools run on the root directory, as well as every request made to the APIs.
#
BDeploy Update
The BDeploy Update page from the Administration menu offers a mechanism to upload new BDeploy software versions and deploy these versions (upgrade and downgrade possible) to the running BDeploy master and attached nodes.
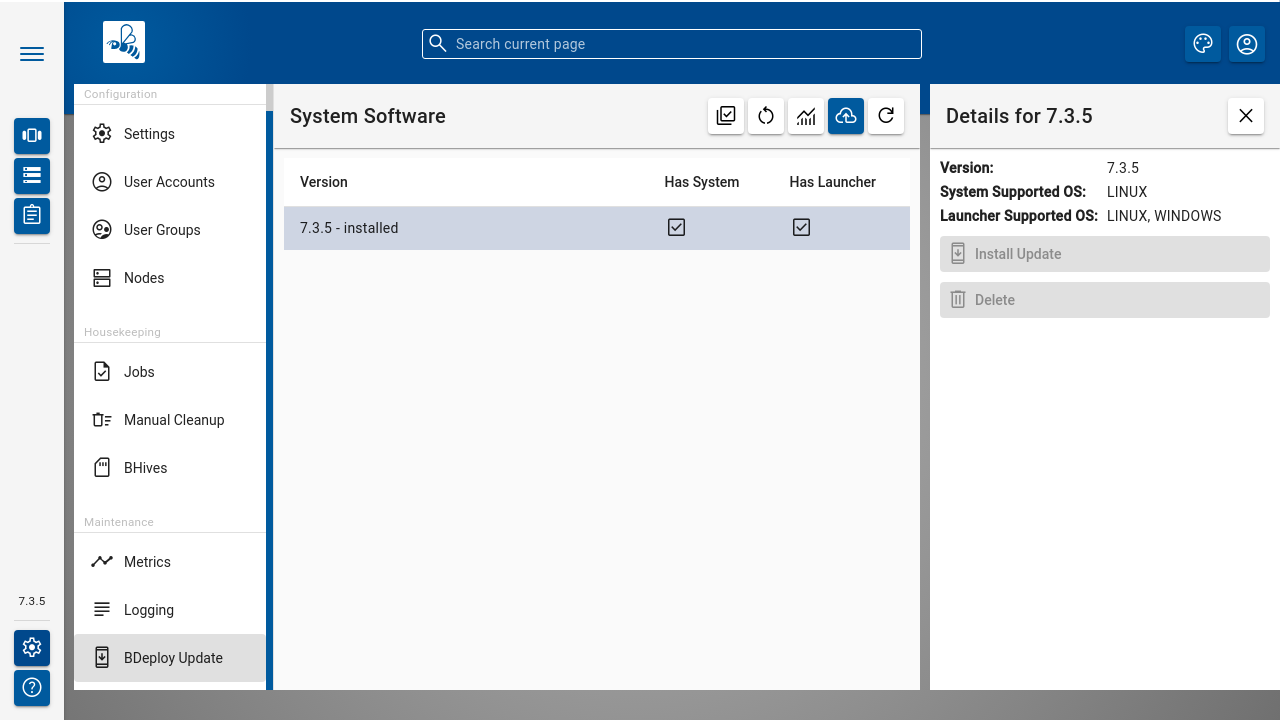
It also offers a way to upload BDeploy Launcher binaries. These binaries are included within a full BDeploy distribution and are required when CLIENT Applications are configured. Usually, a manual upload is not required. In case launchers have been removed by mistake, they can be re-added this way. Use the [ Upload ] button to upload full BDeploy versions or Bdeploy Launcher binaries from the binary distributions (ZIP).

